Classical Civilizations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural
 The
The
 The
The
 The classical period of Ancient Greece corresponds to most of the 5th and 4th centuries BC, in particular, from the fall of the
The classical period of Ancient Greece corresponds to most of the 5th and 4th centuries BC, in particular, from the fall of the
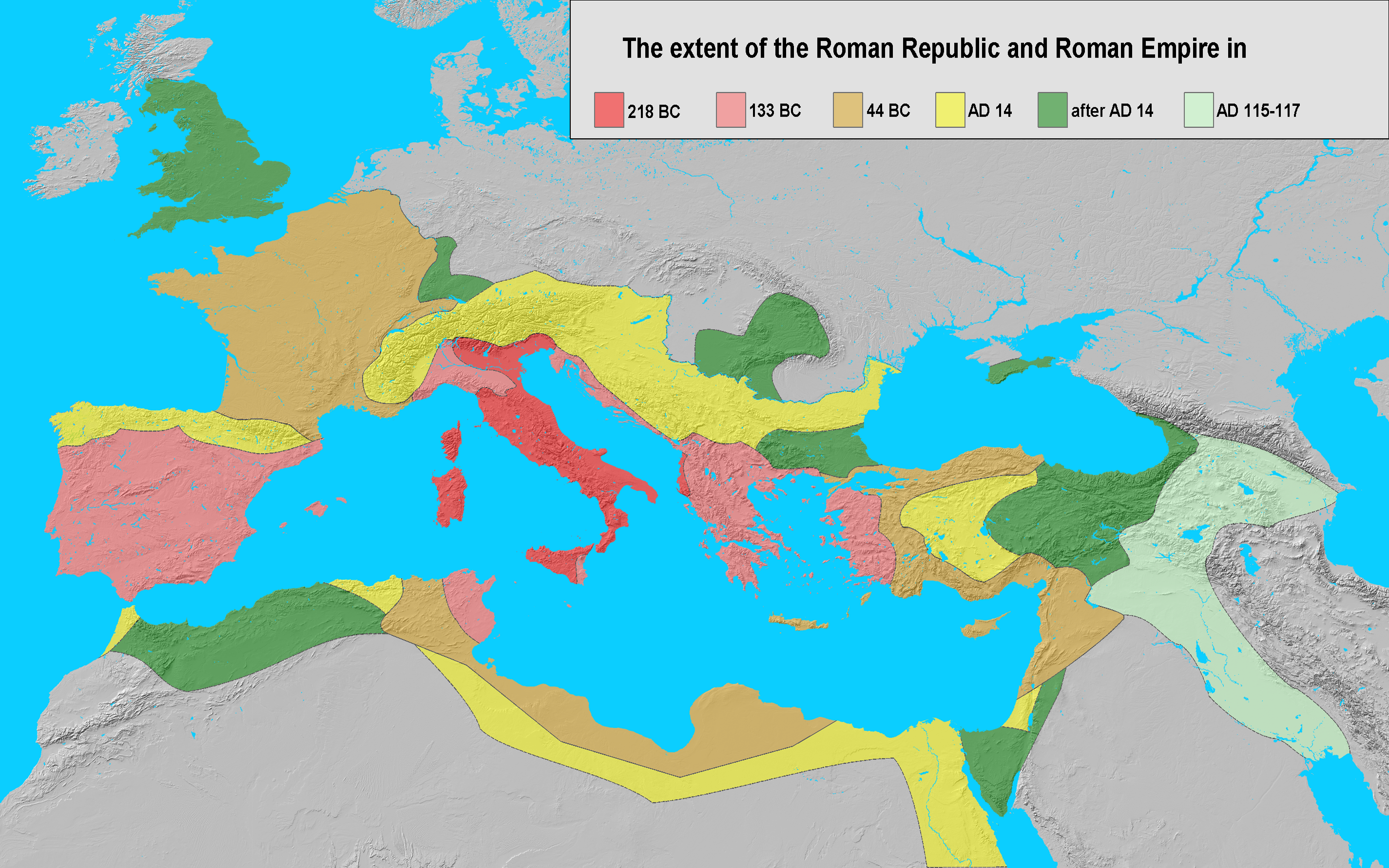 The Roman Republic, Republican period of Ancient Rome began with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom, Monarchy c. 509 BC and lasted over 450 years until its subversion (politics), subversion through a series of Roman Republican civil wars, civil wars, into the Principate form of government and the Imperial period. During the half millennium of the Republic, Rome rose from a regional power of the Latium to the dominant force in Italy and beyond. The unification of Italy under Roman hegemony was a gradual process, brought about in a series of conflicts of the 4th and 3rd centuries, the Samnite Wars, Latin War, and Pyrrhic War. Roman victory in the Punic Wars and Macedonian Wars established Rome as a super-regional power by the 2nd century BC, followed up by the acquisition of Roman Greece, Greece and Asia (Roman province), Asia Minor. This tremendous increase of power was accompanied by economic instability and social unrest, leading to the Second Catilinarian conspiracy, Catiline conspiracy, the Social War (91–88 BC), Social War and the First Triumvirate, and finally the transformation to the Roman Empire in the latter half of the 1st century BC.
The Roman Republic, Republican period of Ancient Rome began with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom, Monarchy c. 509 BC and lasted over 450 years until its subversion (politics), subversion through a series of Roman Republican civil wars, civil wars, into the Principate form of government and the Imperial period. During the half millennium of the Republic, Rome rose from a regional power of the Latium to the dominant force in Italy and beyond. The unification of Italy under Roman hegemony was a gradual process, brought about in a series of conflicts of the 4th and 3rd centuries, the Samnite Wars, Latin War, and Pyrrhic War. Roman victory in the Punic Wars and Macedonian Wars established Rome as a super-regional power by the 2nd century BC, followed up by the acquisition of Roman Greece, Greece and Asia (Roman province), Asia Minor. This tremendous increase of power was accompanied by economic instability and social unrest, leading to the Second Catilinarian conspiracy, Catiline conspiracy, the Social War (91–88 BC), Social War and the First Triumvirate, and finally the transformation to the Roman Empire in the latter half of the 1st century BC.
 The precise end of the Republic is disputed by modern historians; Roman citizens of the time did not recognize that the Republic had ceased to exist. The early Julio-Claudian dynasty, Julio-Claudian Roman Emperor, Emperors maintained that the ''res publica'' still existed, albeit under the protection of their extraordinary powers, and would eventually return to its full Republican form. The Roman state continued to call itself a ''res publica'' as long as it continued to use Latin as its official language.
Rome acquired imperial character ''de facto'' from the 130s BC with the acquisition of Cisalpine Gaul, Illyria, Roman Greece, Greece and Hispania, and definitely with the addition of Iudaea Province, Iudaea, Asia (Roman province), Asia Minor and Roman Gaul, Gaul in the 1st century BC. At the time of the empire's maximal extension under Trajan (AD 117), Rome controlled the entire
The precise end of the Republic is disputed by modern historians; Roman citizens of the time did not recognize that the Republic had ceased to exist. The early Julio-Claudian dynasty, Julio-Claudian Roman Emperor, Emperors maintained that the ''res publica'' still existed, albeit under the protection of their extraordinary powers, and would eventually return to its full Republican form. The Roman state continued to call itself a ''res publica'' as long as it continued to use Latin as its official language.
Rome acquired imperial character ''de facto'' from the 130s BC with the acquisition of Cisalpine Gaul, Illyria, Roman Greece, Greece and Hispania, and definitely with the addition of Iudaea Province, Iudaea, Asia (Roman province), Asia Minor and Roman Gaul, Gaul in the 1st century BC. At the time of the empire's maximal extension under Trajan (AD 117), Rome controlled the entire
 Late antiquity saw the rise of Early Christianity, Christianity under Constantine I, finally ousting the Roman imperial cult with the Theodosian decrees of 393. Successive invasions of Germanic tribes finalized the
Decline of the Roman Empire, decline of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, while the Eastern Roman Empire persisted throughout the Middle Ages, in a state called the Roman Empire by its citizens, and labeled the Byzantine Empire by later historians.
Hellenistic philosophy was succeeded by continued developments in Platonism and Epicureanism, with Neoplatonism in due course influencing the Christian theology, theology of the Church Fathers.
Many writers have attempted to put a specific date on the symbolic "end" of antiquity with the most prominent dates being the deposing of the last Western Roman Emperor in 476, the closing of the last Platonic Academy in Athens by the Eastern Roman Emperor Justinian I in 529, and the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb, conquest of much of the Mediterranean by the new Muslim faith from 634 to 718.Henri Pirenne (1937)
Late antiquity saw the rise of Early Christianity, Christianity under Constantine I, finally ousting the Roman imperial cult with the Theodosian decrees of 393. Successive invasions of Germanic tribes finalized the
Decline of the Roman Empire, decline of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, while the Eastern Roman Empire persisted throughout the Middle Ages, in a state called the Roman Empire by its citizens, and labeled the Byzantine Empire by later historians.
Hellenistic philosophy was succeeded by continued developments in Platonism and Epicureanism, with Neoplatonism in due course influencing the Christian theology, theology of the Church Fathers.
Many writers have attempted to put a specific date on the symbolic "end" of antiquity with the most prominent dates being the deposing of the last Western Roman Emperor in 476, the closing of the last Platonic Academy in Athens by the Eastern Roman Emperor Justinian I in 529, and the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb, conquest of much of the Mediterranean by the new Muslim faith from 634 to 718.Henri Pirenne (1937)
''Mohammed and Charlemagne''
English translation by Bernard Miall, 1939. From Internet Archive. The thesis was originally laid out in an article published in ''Revue Belge de Philologie et d'Histoire'' 1 (1922), pp. 77–86. These Muslim conquests, of Syria (637), Egypt (639), Cyprus (654), North Africa (665), Hispania (718), Southern Gaul (720), Crete (820), and Sicily (827), Malta (870) (and the sieges of the Eastern Roman capital, First Arab Siege of Constantinople (674–78) and Second Arab Siege of Constantinople (717–18)) severed the economic, cultural, and political links that had traditionally united the classical cultures around the Mediterranean, ending antiquity (see Pirenne Thesis). The original Roman Senate continued to express decrees into the late 6th century, and the last Eastern Roman emperor to use
The original Roman Senate continued to express decrees into the late 6th century, and the last Eastern Roman emperor to use
 ''Classical antiquity'' is a broad term for a long period of cultural
''Classical antiquity'' is a broad term for a long period of cultural
Early State in the Classical World
history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
and ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 B ...
known as the Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were di ...
. It is the period in which both Greek and Roman societies flourished and wielded huge influence throughout much of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, and Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
.
Conventionally, it is taken to begin with the earliest-recorded Epic Greek
Homeric Greek is the form of the Greek language that was used by Homer in the ''Iliad'', ''Odyssey'', and Homeric Hymns. It is a literary dialect of Ancient Greek consisting mainly of Ionic, with some Aeolic forms, a few from Arcadocypriot, and a ...
poetry of Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
(8th–7th-century BC), and continues through the emergence of Christianity (1st century AD) and the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Ancient Rome, Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rul ...
(5th-century AD). It ends with the decline of classical culture during late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
(250–750), a period overlapping with the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
(600–1000). Such a wide span of history and territory covers many disparate cultures and periods. ''Classical antiquity'' may also refer to an idealized vision among later people of what was, in Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is wide ...
's words, "the glory that was Greece, and the grandeur that was Rome".
The culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
of the ancient
Ancient history is a time period from the History of writing, beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian language, Sumerian c ...
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, together with some influences from the ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran ( Elam, ...
, was the basis of European art, philosophy, society, and education, until the Roman imperial period
The Roman imperial period is the expansion of political and cultural influence of the Roman Empire. The period begins with the reign of Augustus (), and it is taken to end variously between the late 3rd and the late 4th century, with the beginning ...
. The Romans preserved, imitated, and spread
Spread may refer to:
Places
* Spread, West Virginia
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Spread'' (film), a 2009 film.
* ''$pread'', a quarterly magazine by and for sex workers
* "Spread", a song by OutKast from their 2003 album ''Speakerboxxx/T ...
this culture over Europe, until they themselves were able to compete with it, and the classical world began to speak Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
as well as Greek. This Greco-Roman cultural foundation has been immensely influential on the language, politics, law, educational systems, philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
, science, warfare, poetry, historiography, ethics, rhetoric, art and architecture of the modern world. Surviving fragments of classical culture led to a revival beginning in the 14th century which later came to be known as the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, and various neo-classical revivals occurred in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Archaic period (c. 8th to c. 6th centuries BC)
The earliest period of classical antiquity takes place against the background of gradual re-appearance ofhistorical
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
sources following the Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near Ea ...
. The 8th and 7th centuries BC are still largely proto-historical
Protohistory is a period between prehistory and history during which a culture or civilization has not yet developed writing, but other cultures have already noted the existence of those pre-literate groups in their own writings. For example, in ...
, with the earliest Greek alphabetic inscriptions appearing in the first half of the 8th century. Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
is usually assumed to have lived in the 8th or 7th century BC, and his lifetime is often taken as marking the beginning of classical antiquity. In the same period falls the traditional
A tradition is a belief or behavior (folk custom) passed down within a group or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays or ...
date for the establishment of the Ancient Olympic Games
The ancient Olympic Games (Ὀλυμπιακοὶ ἀγῶνες; la, Olympia, neuter plural: "the Olympics") were a series of athletic competitions among representatives of city-states and were one of the Panhellenic Games of Ancient Greece. ...
, in 776 BC.
Phoenicians, Carthaginians and Assyrians
 The
The Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient thalassocracy, thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-st ...
originally expanded from Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
s, by the 8th century dominating trade in the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
. Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
was founded in 814 BC, and the Carthaginians by 700 BC had firmly established strongholds in Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
and Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after ...
, which created conflicts of interest with Etruria
Etruria () was a region of Central Italy, located in an area that covered part of what are now most of Tuscany, northern Lazio, and northern and western Umbria.
Etruscan Etruria
The ancient people of Etruria
are identified as Etruscan civiliza ...
. A stela
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), whe ...
found in Kition
Kition (Egyptian language, Egyptian: ; Phoenician language, Phoenician: , , or , ; Ancient Greek: , ; Latin: ) was a petty kingdom, city-kingdom on the southern coast of Cyprus (in present-day Larnaca). According to the text on the plaque clos ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
commemorates the victory of King Sargon II
Sargon II (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "the faithful king" or "the legitimate king") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 722 BC to his death in battle in 705. Probably the son of Tiglath-Pileser III (745–727), Sargon is general ...
in 709 BC over the seven kings of the island, marking an important step in the transfer of Cyprus from Tyrian Tyrian may refer to the following:
* Tyrian, an adjective for Tyre, a city in the South Governorate of Lebanon
* ''Tyrian'' (video game), an arcade-style shooter video game by Epic MegaGames
* Tyrian purple, a colour
* Tyrian, a person who worsh ...
rule to the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
.
Greece
The Archaic period followed theGreek Dark Ages
The term Greek Dark Ages refers to the period of Greek history from the end of the Mycenaean palatial civilization, around 1100 BC, to the beginning of the Archaic age, around 750 BC. Archaeological evidence shows a widespread collaps ...
, and saw significant advancements in political theory
Political philosophy or political theory is the philosophical study of government, addressing questions about the nature, scope, and legitimacy of public agents and institutions and the relationships between them. Its topics include politics, l ...
, and the rise of democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose gov ...
, philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
, theatre
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors or actresses, to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The perform ...
, poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings i ...
, as well as the revitalization of the written language (which had been lost during the Dark Ages).
In pottery, the Archaic period sees the development of the Orientalizing style, which signals a shift from the Geometric style
Geometric art is a phase of Greek art, characterized largely by geometric motifs in vase painting, that flourished towards the end of the Greek Dark Ages, . Its center was in Athens, and from there the style spread among the trading cities of the ...
of the later Dark Ages and the accumulation of influences derived from Egypt, Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
.
Pottery styles associated with the later part of the Archaic age are the black-figure pottery
Black-figure pottery painting, also known as the black-figure style or black-figure ceramic ( grc, , }), is one of the styles of painting on antique Greek vases. It was especially common between the 7th and 5th centuries BCE, although there are ...
, which originated in Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
during the 7th-century BC and its successor, the red-figure style, developed by the Andokides Painter
Andokides was an ancient Athenian vase painter, active from approximately 530 to 515 B.C. His work is unsigned and his true name unknown. He was identified as a unique artistic personality through stylistic traits found in common among several pai ...
in about 530 BC.
Greek colonies
Iron Age Italy
 The
The Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, rou ...
had established political control in the region by the late 7th-century BC, forming the aristocratic and monarchial elite. The Etruscans apparently lost power in the area by the late 6th-century BC, and at this point, the Italic tribes reinvented their government by creating a republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
, with much greater restraints on the ability of rulers to exercise power.
Roman Kingdom
According to legend, Rome was founded on 21 April 753 BC by twin descendants of theTrojan
Trojan or Trojans may refer to:
* Of or from the ancient city of Troy
* Trojan language, the language of the historical Trojans
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Les Troyens'' ('The Trojans'), an opera by Berlioz, premiered part 1863, part 1890 ...
prince Aeneas
In Greco-Roman mythology, Aeneas (, ; from ) was a Trojan hero, the son of the Trojan prince Anchises and the Greek goddess Aphrodite (equivalent to the Roman Venus). His father was a first cousin of King Priam of Troy (both being grandsons ...
, Romulus and Remus
In Roman mythology, Romulus and Remus (, ) are twin brothers whose story tells of the events that led to the founding of the city of Rome and the Roman Kingdom by Romulus, following his fratricide of Remus. The image of a she-wolf suckling the ...
. As the city was bereft of women, legend says that the Latins invited the Sabines
The Sabines (; lat, Sabini; it, Sabini, all exonyms) were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome.
The Sabines divid ...
to a festival and stole their unmarried maidens, leading to the integration of the Latins and the Sabines.
Archaeological evidence indeed shows first traces of settlement at the Roman Forum
The Roman Forum, also known by its Latin name Forum Romanum ( it, Foro Romano), is a rectangular forum (plaza) surrounded by the ruins of several important ancient government buildings at the center of the city of Rome. Citizens of the ancient ...
in the mid-8th BC, though settlements on the Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; la, Collis Palatium or Mons Palatinus; it, Palatino ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city and has been called "the first nucleus of the Roman Empire." ...
may date back to the 10th century BC.
The seventh and final king of Rome was Tarquinius Superbus
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (died 495 BC) was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic.Livy, ''ab urbe condita libri'', I He is commonly known a ...
. As the son of Tarquinius Priscus
Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, or Tarquin the Elder, was the legendary fifth king of Rome and first of its Etruscan dynasty. He reigned for thirty-eight years.Livy, ''ab urbe condita libri'', I Tarquinius expanded Roman power through military conqu ...
and the son-in-law of Servius Tullius
Servius Tullius was the legendary sixth king of Rome, and the second of its Etruscan dynasty. He reigned from 578 to 535 BC. Roman and Greek sources describe his servile origins and later marriage to a daughter of Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, Rome ...
, Superbus was of Etruscan birth. It was during his reign that the Etruscans reached their apex of power. Superbus removed and destroyed all the Sabine shrines and altars from the Tarpeian Rock
The Tarpeian Rock (; Latin: ' or '; it, Rupe Tarpea) is a steep cliff on the south side of the Capitoline Hill, which was used in Ancient Rome as a site of execution. Murderers, traitors, perjurors, and larcenous slaves, if convicted by the '' ...
, enraging the people of Rome. The people came to object to his rule when he failed to recognize the rape of Lucretia
According to Roman tradition, Lucretia ( /luːˈkriːʃə/ ''loo-KREE-shə'', Classical Latin: ʊˈkreːtɪ.a died c. 510 BC), anglicized as Lucrece, was a noblewoman in ancient Rome, whose rape by Sextus Tarquinius (Tarquin) and subseq ...
, a patrician Roman, at the hands of his own son. Lucretia's kinsman, Lucius Junius Brutus
Lucius Junius Brutus ( 6th century BC) was the semi-legendary founder of the Roman Republic, and traditionally one of its first consuls in 509 BC. He was reputedly responsible for the expulsion of his uncle the Roman king Tarquinius Superbus after ...
(ancestor to Marcus Brutus
Marcus Junius Brutus (; ; 85 BC – 23 October 42 BC), often referred to simply as Brutus, was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Serv ...
), summoned the Senate and had Superbus and the monarchy expelled from Rome in 510 BC. After Superbus' expulsion, the Senate in 509 BC voted to never again allow the rule of a king and reformed Rome into a republican government
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy, is a type of democracy where elected people represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies function as some type of represe ...
.
Classical Greece (5th to 4th centuries BC)
Athenian tyranny
In ancient Greece the chief magistrate in various Greek city states was called eponymous archon (ἐπώνυμος ἄρχων, ''epōnymos archōn''). "Archon" (ἄρχων, pl. ἄρχοντες, ''archontes'') means "ruler" or "lord", frequently ...
in 510 BC to the death of Alexander the Great
The death of Alexander the Great and subsequent related events have been the subjects of debates. According to a Babylonian astronomical diaries, Babylonian astronomical diary, Alexander died in the palace of Nebuchadnezzar II in Babylon betwee ...
in 323 BC. In 510, Spartan troops helped the Athenians overthrow the tyrant Hippias
Hippias of Elis (; el, Ἱππίας ὁ Ἠλεῖος; late 5th century BC) was a Greek sophist, and a contemporary of Socrates. With an assurance characteristic of the later sophists, he claimed to be regarded as an authority on all subjects, ...
, son of Peisistratos
Pisistratus or Peisistratus ( grc-gre, Πεισίστρατος ; 600 – 527 BC) was a politician in ancient Athens, ruling as tyrant in the late 560s, the early 550s and from 546 BC until his death. His unification of Attica, the triangular ...
. Cleomenes I
Cleomenes I (; Greek Κλεομένης; died c. 490 BC) was Agiad King of Sparta from c. 524 to c. 490 BC. One of the most important Spartan kings, Cleomenes was instrumental in organising the Greek resistance against the Persian Empire of Dariu ...
, king of Sparta, put in place a pro-Spartan oligarchy conducted by Isagoras
Isagoras ( grc-gre, Ἰσαγόρας), son of Tisander, was an Athenian aristocrat in the late 6th century BC.
He had remained in Athens during the tyranny of Hippias, but after Hippias was overthrown, he became involved in a struggle for power ...
.
The Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the ...
(499–449 BC), concluded by the Peace of Callias
The Peace of Callias is a purported peace treaty established around 449 BC between the Delian League (led by Athens) and Persia, ending the Greco-Persian Wars. The peace was agreed as the first compromise treaty between Achaemenid Persia and a Gree ...
gave way not only to the liberation of Greece, Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
, Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
, and Ionia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionian ...
from Persian rule, but also resulted in giving the dominant position of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
in the Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pl ...
, which led to conflict with Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
and the Peloponnesian League
The Peloponnesian League was an alliance of ancient Greek city-states, dominated by Sparta and centred on the Peloponnese, which lasted from c.550 to 366 BC. It is known mainly for being one of the two rivals in the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC ...
, resulting in the Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
(431–404 BC), ending in a Spartan victory.
Greece entered the 4th century under Spartan hegemony
The polis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Lat ...
, but by 395 BC the Spartan rulers removed Lysander
Lysander (; grc-gre, Λύσανδρος ; died 395 BC) was a Spartan military and political leader. He destroyed the Athenian fleet at the Battle of Aegospotami in 405 BC, forcing Athens to capitulate and bringing the Peloponnesian War to an en ...
from office, and Sparta lost her naval supremacy. Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, Argos
Argos most often refers to:
* Argos, Peloponnese, a city in Argolis, Greece
** Ancient Argos, the ancient city
* Argos (retailer), a catalogue retailer operating in the United Kingdom and Ireland
Argos or ARGOS may also refer to:
Businesses
...
, Thebes and Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
, the latter two of which were formerly Spartan allies, challenged Spartan dominance in the Corinthian War
The Corinthian War (395–387 BC) was a conflict in ancient Greece which pitted Sparta against a coalition of city-states comprising Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos, backed by the Achaemenid Empire. The war was caused by dissatisfaction with ...
, which ended inconclusively in 387 BC. Later, in 371 BC, the Theban generals Epaminondas
Epaminondas (; grc-gre, Ἐπαμεινώνδας; 419/411–362 BC) was a Greek general of Thebes and statesman of the 4th century BC who transformed the Ancient Greek city-state, leading it out of Spartan subjugation into a pre-eminent posit ...
and Pelopidas
Pelopidas (; grc-gre, Πελοπίδας; died 364 BC) was an important Theban statesman and general in Greece, instrumental in establishing the mid-fourth century Theban hegemony.
Biography
Athlete and warrior
Pelopidas was a member of a ...
won a victory at the Battle of Leuctra
The Battle of Leuctra ( grc-gre, Λεῦκτρα, ) was a battle fought on 6 July 371 BC between the Boeotians led by the Thebans, and the Spartans along with their allies amidst the post-Corinthian War conflict. The battle took place in the vicin ...
. The result of this battle was the end of Spartan supremacy and the establishment of Theban hegemony
The Theban hegemony lasted from the Theban victory over the Spartans at Leuctra in 371 BC to their defeat of a coalition of Peloponnesian armies at Mantinea in 362 BC, though Thebes sought to maintain its position until finally eclipsed by the ...
. Thebes sought to maintain its position until it was finally eclipsed by the rising power of Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
in 346 BC.
Under Philip II, (359–336 BC), Macedon expanded into the territory of the Paeonians
Paeonians were an ancient Indo-European people that dwelt in Paeonia. Paeonia was an old country whose location was to the north of Ancient Macedonia, to the south of Dardania, to the west of Thrace and to the east of Illyria, most of their lan ...
, the Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
and the Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo ...
. Philip's son, Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
, (356–323 BC) managed to briefly extend Macedonian power not only over the central Greek city-states but also to the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
, including Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
and lands as far east as the fringes of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. The classical period conventionally ends at the death of Alexander in 323 BC and the fragmentation of his empire, which was at this time divided among the Diadochi
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The War ...
.
Hellenistic period (323–146 BC)
Classical Greece entered the Hellenistic period with the rise ofMacedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
and the conquests of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
. Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
became the ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
'' far beyond Greece itself, and Hellenistic culture interacted with the cultures of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel and Kingdom of Judah, Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Central Asia and Ptolemaic Egypt, Egypt. Significant advances were made in the sciences (Ancient Greek geography, geography, Greek astronomy, astronomy, Greek mathematics, mathematics, etc.), notably with the Peripatetic school, followers of Aristotle (Aristotelianism).
The Hellenistic period ended with the rise of the Roman Republic to a super-regional power in the 2nd century BC and the Roman conquest of Greece in 146 BC.
Roman Republic (5th to 1st centuries BC)
 The Roman Republic, Republican period of Ancient Rome began with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom, Monarchy c. 509 BC and lasted over 450 years until its subversion (politics), subversion through a series of Roman Republican civil wars, civil wars, into the Principate form of government and the Imperial period. During the half millennium of the Republic, Rome rose from a regional power of the Latium to the dominant force in Italy and beyond. The unification of Italy under Roman hegemony was a gradual process, brought about in a series of conflicts of the 4th and 3rd centuries, the Samnite Wars, Latin War, and Pyrrhic War. Roman victory in the Punic Wars and Macedonian Wars established Rome as a super-regional power by the 2nd century BC, followed up by the acquisition of Roman Greece, Greece and Asia (Roman province), Asia Minor. This tremendous increase of power was accompanied by economic instability and social unrest, leading to the Second Catilinarian conspiracy, Catiline conspiracy, the Social War (91–88 BC), Social War and the First Triumvirate, and finally the transformation to the Roman Empire in the latter half of the 1st century BC.
The Roman Republic, Republican period of Ancient Rome began with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom, Monarchy c. 509 BC and lasted over 450 years until its subversion (politics), subversion through a series of Roman Republican civil wars, civil wars, into the Principate form of government and the Imperial period. During the half millennium of the Republic, Rome rose from a regional power of the Latium to the dominant force in Italy and beyond. The unification of Italy under Roman hegemony was a gradual process, brought about in a series of conflicts of the 4th and 3rd centuries, the Samnite Wars, Latin War, and Pyrrhic War. Roman victory in the Punic Wars and Macedonian Wars established Rome as a super-regional power by the 2nd century BC, followed up by the acquisition of Roman Greece, Greece and Asia (Roman province), Asia Minor. This tremendous increase of power was accompanied by economic instability and social unrest, leading to the Second Catilinarian conspiracy, Catiline conspiracy, the Social War (91–88 BC), Social War and the First Triumvirate, and finally the transformation to the Roman Empire in the latter half of the 1st century BC.
Roman Empire (1st century BC to 5th century AD)
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
as well as Gaul, parts of Germania and Roman Britain, Britannia, the Balkans, Dacia, Asia Minor, the Caucasus, and Mesopotamia.
Culturally, the Roman Empire was significantly Hellenization, Hellenized, but also saw the rise of syncretic "eastern" traditions, such as Mithraism, Gnosticism, and most notably Origins of Christianity, Christianity.
The empire began to decline in the crisis of the third century.
While sometimes compared with classical Greece, classical Rome had vast differences within their family life. Fathers had great power over their children, and husbands over their wives. In fact, the word family, ''familia'' in Latin, actually referred to those who were under the authority of a male head of household. This included non-related members such as slaves and servants. In marriage, both men and women were loyal to one another and shared property. Divorce was first allowed starting in the first century BC and could be done by either man or woman.
Late antiquity (4th to 6th centuries AD)
''Mohammed and Charlemagne''
English translation by Bernard Miall, 1939. From Internet Archive. The thesis was originally laid out in an article published in ''Revue Belge de Philologie et d'Histoire'' 1 (1922), pp. 77–86. These Muslim conquests, of Syria (637), Egypt (639), Cyprus (654), North Africa (665), Hispania (718), Southern Gaul (720), Crete (820), and Sicily (827), Malta (870) (and the sieges of the Eastern Roman capital, First Arab Siege of Constantinople (674–78) and Second Arab Siege of Constantinople (717–18)) severed the economic, cultural, and political links that had traditionally united the classical cultures around the Mediterranean, ending antiquity (see Pirenne Thesis).
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
as the language of his court in Constantinople was emperor Maurice (emperor), Maurice, who reigned until 602. The overthrow of Maurice by his mutinying Danube army under Phocas resulted in the Slavic invasion of the Balkans and the decline of Balkan and Greek urban culture (leading to the flight of Balkan Latin speakers to the mountains, see Origin of the Romanians), and also provoked the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628 in which all the great eastern cities except Constantinople were lost. The resulting turmoil did not end until the Muslim conquests of the 7th century finalized the irreversible loss of all the largest Eastern Roman imperial cities besides the capital itself. The emperor Heraclius in Constantinople, who emerged during this period, conducted his court in Greek, not Latin, though Greek had always been an administrative language of the eastern Roman regions. Eastern-Western links weakened with the ending of the Byzantine Papacy.
The Eastern Roman empire's capital city of Constantinople was left as the only unconquered large urban center of the original Roman empire, as well as being the largest city in Europe. Yet many classical books, sculptures, and technologies survived there along with classical Roman cuisine and scholarly traditions, well into the Middle Ages, when much of it was "rediscovered" by visiting Western crusaders. Indeed, the inhabitants of Constantinople continued to refer to themselves as Romans, as did their eventual conquerors in 1453, the Ottomans. (see Rûm and Romaioi.) The classical scholarship and culture that was still preserved in Constantinople were brought by refugees fleeing its conquest in 1453 and helped to spark the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
(see Greek scholars in the Renaissance).
Ultimately, it was a slow, complex, and graduated change in the socio-economic structure in European history that led to the changeover between Classical antiquity and Medieval society and no specific date can truly exemplify that.
Political revivalism
In politics, the late Roman conception of the Empire as a universal state, headed by one supreme divinely appointed ruler, united with Christianity as a universal religion likewise headed by a supreme patriarch, proved very influential, even after the disappearance of imperial authority in the west. This tendency reached its peak when Charlemagne was Coronation, crowned "Roman Emperor" in the year 800, an act which led to the formation of the Holy Roman Empire. The notion that an emperor is a monarch who outranks a mere king dates from this period. In this political ideal, there would always be a Roman Empire, a state whose jurisdiction extended through the entire civilized western world. That model continued to exist in Constantinople for the entirety of the Middle Ages; the Byzantine Emperor was considered the sovereign of the entire Christian world. The Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople, Patriarch of Constantinople was the Empire's highest-ranked cleric, but even he was subordinate to the emperor, who was "God's Vicegerent on Earth". The Greek-speaking Byzantines and their descendants Romioi, continued to call themselves "Romans" until the creation of a new Greek state in 1832. After the fall of Constantinople in 1453, the Russian Czar of Russia, Czars (a title derived from ''Caesar)'' claimed the Byzantine mantle as the champion of Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodoxy; Moscow was described as the "Third Rome" and the Czars ruled as divinely appointed Emperors into the 20th century. Despite the fact that the Western Roman secular authority disappeared entirely in Europe, it still left traces. The Papacy and the Catholic Church in particular maintained Latin language, culture, and literacy for centuries; to this day the popes are called ''Pontifex Maximus'' which in the classical period was a title belonging to the emperor, and the ideal of Christendom carried on the legacy of a united European civilization even after its political unity had disappeared. The political idea of an Emperor in the West to match the Emperor in the East continued after the Western Roman Empire's collapse; it was revived by the coronation of Charlemagne in 800; the self-described Holy Roman Empire ruled over central Europe until 1806. TheRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
idea that the classical Roman virtues had been lost under medievalism was especially powerful in European politics of the 18th and 19th centuries. Reverence for Roman republicanism was strong among the Founding Fathers of the United States and the Latin American revolutionaries; the Americans described their new government as a ''republic'' (from ''res publica'') and gave it a ''Senate'' and a ''President'' (another Latin term), rather than make use of available English terms like ''commonwealth'' or ''parliament''.
Similarly in French Revolution, Revolutionary and First French Empire, Napoleonic France, republicanism and Roman martial virtues were upheld by the state, as can be seen in the architecture of the Panthéon, Paris, Panthéon, the Arc de Triomphe, and the paintings of Jacques-Louis David. During the revolution, France itself followed the transition from kingdom to republic to dictatorship to Empire (complete with Imperial Eagles) that Rome had undergone centuries earlier.
Cultural legacy
 ''Classical antiquity'' is a broad term for a long period of cultural
''Classical antiquity'' is a broad term for a long period of cultural history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
. Such a wide sampling of history and territory covers many rather disparate cultures and periods. "Classical antiquity" often refers to an idealized vision of later people, of what was, in Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is wide ...
's words, the glory that was Ancient Greece, Greece, the grandeur that was Ancient Rome, Rome!In the 18th and 19th centuries AD, reverence for classical antiquity was much greater in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and the United States than it is today. Respect for the ancient people of Greece and Rome affected politics, philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
, sculpture, literature, theatre
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors or actresses, to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The perform ...
, education, architecture, and History of sex, sexuality.
Epic poetry in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
continued to be written and circulated well into the 19th century. John Milton and even Arthur Rimbaud received their first poetic educations in Latin. Genres like epic poetry, pastoral verse, and the endless use of characters and themes from Greek mythology left a deep mark on Western literature. In architecture, there have been several Greek Revivals, which seem more inspired in retrospect by Roman architecture than Greek. Washington, DC is filled with large marble buildings with facades made out to look like Greek temples, with columns constructed in the classical orders of architecture.
In philosophy, the thought of St. Thomas Aquinas was derived largely from that of Aristotle, despite the intervening change in religion from Hellenistic religion, Hellenic Polytheism to Christianity. Greek and Roman authorities such as Hippocrates and Galen formed the foundation of the practice of medicine even longer than Greek thought prevailed in philosophy. In the France, French theater, tragedy, tragedians such as Molière and Jean Racine, Racine wrote plays on mythological or classical historical subjects and subjected them to the strict rules of the classical unities derived from Aristotle's ''Poetics (Aristotle), Poetics''. The desire to dance like a latter-day vision of how the ancient Greeks did moved Isadora Duncan to create her brand of ballet.
Timeline
See also
* Classical architecture * Classical tradition * Classics (Classical education) * Outline of classical studies ** Outline of ancient Egypt ** Outline of ancient Greece ** Outline of ancient Rome * Postclassical Era (the next period) ; Regions during classical antiquity * Ancient history of Cyprus * Hellenistic Greece * History of the Balkans * Roman Britain * Roman Dacia * TroyNotes
References
Citations
Sources
* Grinin L. E. Early State in the Classical World: Statehood and Ancient Democracy. In Grinin L. E. et al. (eds.) Hierarchy and Power in the History of civilizations: Ancient and Medieval Cultures 9pp.31–84). Moscow: URSS, 200Early State in the Classical World
Further reading
*Boatwright, Mary T., Daniel J. Gargola, and Richard J. A. Talbert. 2004. ''The Romans: From village to empire.'' New York and Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press *Bugh, Glenn. R., ed. 2006. ''The Cambridge Companion to the Hellenistic world.'' Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press. *Burkert, Walter. 1992. ''The Orientalizing revolution: The Near Eastern influence on Greek culture in the early Archaic age.'' Translated by Margaret E. Pinder and Walter Burkert. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Univ. Press. *Erskine, Andrew, ed. 2003. ''A companion to the Hellenistic world.'' Malden, MA, and Oxford: Blackwell. *Flower, Harriet I. 2004. ''The Cambridge Companion to the Roman Republic.'' Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press. *Green, Peter. 1990. ''Alexander to Actium: The historical evolution of the Hellenistic age.'' Berkeley: Univ. of California Press. *Hornblower, Simon. 1983. ''The Greek world 479–323 BC.'' London and New York: Methuen. *Kallendorf, Craig W., ed. 2007. ''A Companion to the Classical Tradition.'' Malden, MA: Blackwell. *Kinzl, Konrad, ed. 2006. ''A Companion to the Classical Greek world.'' Oxford and Malden, MA: Blackwell. *Murray, Oswyn. 1993. ''Early Greece.'' 2nd ed. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Univ. Press. *Potter, David S. 2006. ''A companion to the Roman Empire.'' Malden, MA: Blackwell *Rhodes, Peter J. 2006. ''A history of the Classical Greek world: 478–323 BC.'' Blackwell History of the Ancient World. Malden, MA: Blackwell. *Rosenstein, Nathan S., and Robert Morstein-Marx, eds. 2006. ''A companion to the Roman Republic.'' Oxford: Blackwell. *Shapiro, H. Alan, ed. 2007. ''The Cambridge Companion to Archaic Greece.'' Cambridge Companions to the Ancient World. Cambridge, UK, and New York: Cambridge Univ. Press. *Shipley, Graham. 2000. ''The Greek world after Alexander 323–30 BC.'' London: Routledge. *Walbank, Frank W. 1993. ''The Hellenistic world.'' Revised ed. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Univ. Press. {{DEFAULTSORT:Classical Antiquity Classical antiquity, History of the Mediterranean History of Europe by period Articles which contain graphical timelines Historical eras